HA is a naturally occurring polymer found in connective, neural, and epithelial tissue in both animals and humans. Hyaluronic Acid can hold about 1,000 times its weight in water.
Because of its ability to hold water, HA is an easy choice when looking for an ingredient that will hold moisture when applied to the skin.
Product name: Hyaluronic Acid
CAS #: 9004-61-9
EC #: 232-678-0
EF: (C14H21NO11)n

| Property Name |
Property Value |
| Molecular Weight |
846.8 g/mol |
| XLogP3-AA |
-6.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
14 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
23 |
| Rotatable Bond Count |
16 |
| Exact Mass |
846.311736 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass |
846.311736 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area |
400 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count |
58 |
| Formal Charge |
0 |
| Hyaluronic acid Usage And Synthesis |
| Hyaluronic Acid |
Hyaluronic acid is a completely transparent, non-adhesive, water-soluble and grease-free acid mucopolysaccharide. Its molecular weight is between a few hundred thousand to millions, and it makes up the dermis layer of the skin. Its unique molecular structure and physicochemical properties has many important physiological functions inside the body, such as lubricating joints, adjusting vascular permeability, adjusting proteins, diffusing and transporting water electrolytes, and promoting wound healing. Hyaluronic acid has a unique water retention effect and has the best-known natural moisturizing properties, making it the ideal natural moisturizer.
Hyaluronic acid is an essential drug in ophthalmic “sticky surgeries”. It is used in cataract surgery, in which its sodium salt remains in the anterior chamber to maintain depth in the anterior chamber and ensure a clear surgical view. It reduces the occurrences of postoperative inflammation and complications, thus improving the vision-correcting effects of the surgery. It is also used in complicated retinol detachment surgery. Figure 1. Three types of medical applications of hyaluronan. HA, hyaluronan; OA, osteoarthritis; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection. The italic indicates future medical applications.
Hyaluronic acid has a low molecular weight and is considered the ideal natural moisturizing agent, so it is used as an additive in high-end makeup and as a moisturizer in creams, gels, lotions, masks, and serums. It is also used medically as a moisturizer to improve moisture retention and lubrication, and it also expands capillaries and improves skin health. For example, hyaluronic acid with a low molecular weight can be used as a lubricant in surgeries(such as knee surgery), while those with high molecular weight can be used as surgical lubricant and as a substitute for vitreous in ophthalmic surgery.
Figure 1. Three types of medical applications of hyaluronan. HA, hyaluronan; OA, osteoarthritis; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection. The italic indicates future medical applications.
Hyaluronic acid has a low molecular weight and is considered the ideal natural moisturizing agent, so it is used as an additive in high-end makeup and as a moisturizer in creams, gels, lotions, masks, and serums. It is also used medically as a moisturizer to improve moisture retention and lubrication, and it also expands capillaries and improves skin health. For example, hyaluronic acid with a low molecular weight can be used as a lubricant in surgeries(such as knee surgery), while those with high molecular weight can be used as surgical lubricant and as a substitute for vitreous in ophthalmic surgery. |
| Benefits |
Hyaluronic acid’s main functions include:
Has excellent affinity to water and can regroup water within tissue for better retention and lubrication.
Folds to form a three-dimensional network and produces physiological effects, including producing fluid resistance, maintaining water balance and bodily stability, influencing macromolecule solubility, structure, chemical balance and system osmotic pressure, preventing the spread of pathogens, and promote the condensation of collagen fiber secretory substances.
Forms polymers with inseparable proteins to maintain tissue shape and size and to ensure reversible tissue compression resistance.
Affects macrophages, adherent cells, lymph cells, and natural killer cells.
Serves as an important part of interstitial fluid and is mainly metabolized in the liver. Liver fiber activity increases HA synthesis; combined with reduced function during cirrhosis, blood HA levels may increase abnormally. |
| Uses |
Synovitis agent(veterinary). |
| Uses |
hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan component. Hyaluronic acid occurs naturally in the dermis. It is thought to play a critical role in healthy skin by controlling the physical and biochemical characteristics of epidermal cells. It also regulates general skin activity, such as water content, elasticity, and the distribution of nutrients. Its water-absorption abilities and large molecular structure allow the epidermis to achieve greater suppleness, proper plasticity, and turgor. Hyaluronic acid is a natural moisturizer with excellent water-binding capabilities. In a solution of 2 percent hyaluronic acid and 98 percent water, the hyaluronic acid holds the water so tightly that it appears to create a gel. However, it is a true liquid in that it can be diluted and will exhibit a liquid’s normal viscous flow properties.
 Figure 2.The water molecules which are hydrogen-bonded to HA stabilize the surfactant layer
When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behaviour suggest that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different.
Figure 2.The water molecules which are hydrogen-bonded to HA stabilize the surfactant layer
When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behaviour suggest that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different. |
| Definition |
hyaluronic acid: A glycosaminoglycan( mucopolysaccharide) that is part of the matrix of connective tissue. Hyaluronic acid binds cells together and helps to lubricate joints. It may play a role in the migration of cells at wounds; this activity ceases when hyaluronidase breaks down hyaluronic acid.
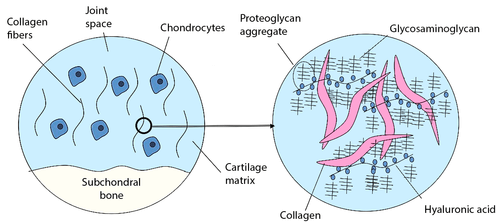 Figure no 3. The cartilage matrix. The joint space is filled with synovial fluid. Glycosaminoglycans are attached to proteins, which are attached to a strand of hyaluronic acid to create a "bottle brush".
Figure no 3. The cartilage matrix. The joint space is filled with synovial fluid. Glycosaminoglycans are attached to proteins, which are attached to a strand of hyaluronic acid to create a "bottle brush". |
|
Veterinary
Drugs and
Treatments
|
Hyaluronic acid is a natural complex sugar of the glycosaminoglycan family and is a long-chain polymer containing repeating disaccharide units of Na-glucuronate-N-acetylglucosamine.
 Figure 4. Hyaluronic acid is composed of alternating residues of β-D-(1‑3) glucuronic acid and β-D-(1‑4)-N-acetylglucosamine.
Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction(intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues.
Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuverer and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation.
Figure 4. Hyaluronic acid is composed of alternating residues of β-D-(1‑3) glucuronic acid and β-D-(1‑4)-N-acetylglucosamine.
Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction(intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues.
Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuverer and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation. |
HA Extraction:
Hyaluronic acid is a substance that is naturally present in the human body. It is found in the highest concentrations in fluids in the
eyes and joints. The hyaluronic acid that is used as medicine is extracted from rooster combs or made by bacteria in the laboratory.
Today, most HA is from vegan sources like the
Hyaluronic Acid Powder used and sold by Essential, and safe to use. In 2003, the FDA even approved HA as an injectable in anti-aging treatments. While these treatments are effective, they are often very expensive and only last for about 4-6 months.
HA Benefits:
 Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
It is the result of two biologically independent processes. The first is intrinsic or innate aging, an unpreventable process, which affects the skin in the same pattern as it affects all internal organs. The second is extrinsic aging, which is the result of exposure to external factors, mainly ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, that is also referred to as photoaging.
Skin aging is also associated with loss of skin moisture. The key molecule involved in skin moisture is hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a unique capacity to bind and retain water molecules.
Promotes Healthier, More Supple Skin:

Hyaluronic acid supplements can help increase skin moisture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical treatments can soothe redness and dermatitis, while injections can make skin appear firmer.
Can Speed Wound Healing:
Applying hyaluronic acid directly to an open wound can help speed up the recovery process. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effect.
Relieve Joint Pain by Keeping Bones Well Lubricated:
Hyaluronic acid supplements are effective at reducing joint pain in people with osteoarthritis. Injections can also be used but may come with risks.
 Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
A combination supplement containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate may help reduce the symptoms of acid reflux in some people.
Relieve Dry Eye and Discomfort:

Hyaluronic acid is naturally found in the eyes and often an ingredient in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effects.
Preserve Bone Strength:
Animal and test-tube research suggest that high doses of hyaluronic acid may help prevent bone loss, but no research has been conducted in humans.
Could Prevent Bladder Pain:
Hyaluronic acid can relieve bladder pain when inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter, but taking supplements by mouth may not have the same effects.
Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare Formulations:
Fortunately, when hyaluronic acid is applied topically, it takes very little to make a noticeable difference in helping aging skin recapture the appearance of youthful skin. In fact, it is so effective at retaining moisture it’s nearly impossible to add more than
2% HA to any formulation.
Sodium hyaluronate, another ingredient, is a salt that is derived from hyaluronic acid. The biggest difference between the two is that sodium hyaluronate absorbs into the skin much more readily than hyaluronic acid does.
- wound healing
- anti-wrinkle
- increases skin elasticity
- can treat eczema
- can treat facial redness
 Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Hyaluronic acid is generally very safe to use, with few reported side effects.
Since the body naturally produces it, allergic reactions are very rare.
One study in 60 people with osteoarthritis who took 200 mg daily for one year reported no negative side effects.
However, its effects during pregnancy or breastfeeding have not been thoroughly studied, so these groups should be cautious and avoid supplementing with it.
There is also some evidence that cancer cells are sensitive to hyaluronic acid and taking supplements could make them grow faster.
For this reason, it is generally advised that people with cancer or a history of cancer avoid supplementing with it.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the skin or joints have a higher risk of side effects. However, negative reactions are mostly associated with the injection procedure, rather than hyaluronic acid itself.

Summary:
> Hyaluronic acid supplements can be safely taken by most people and provide many health benefits.
> Hyaluronic acid is well known for its skin benefits, especially alleviating dry skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and speeding up wound healing.
> It can also help relieve joint pain in people with osteoarthritis.
> Other notable applications include hyaluronic acid eye drops to relieve dry eye and inserting hyaluronic acid directly into the bladder via catheter to reduce pain.
> Overall, hyaluronic acid is a beneficial supplement for a variety of conditions, especially those related to skin and joint health.


 Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
It is the result of two biologically independent processes. The first is intrinsic or innate aging, an unpreventable process, which affects the skin in the same pattern as it affects all internal organs. The second is extrinsic aging, which is the result of exposure to external factors, mainly ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, that is also referred to as photoaging.
Skin aging is also associated with loss of skin moisture. The key molecule involved in skin moisture is hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a unique capacity to bind and retain water molecules.
Promotes Healthier, More Supple Skin:
Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
It is the result of two biologically independent processes. The first is intrinsic or innate aging, an unpreventable process, which affects the skin in the same pattern as it affects all internal organs. The second is extrinsic aging, which is the result of exposure to external factors, mainly ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, that is also referred to as photoaging.
Skin aging is also associated with loss of skin moisture. The key molecule involved in skin moisture is hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a unique capacity to bind and retain water molecules.
Promotes Healthier, More Supple Skin:
 Hyaluronic acid supplements can help increase skin moisture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical treatments can soothe redness and dermatitis, while injections can make skin appear firmer.
Can Speed Wound Healing:
Applying hyaluronic acid directly to an open wound can help speed up the recovery process. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effect.
Relieve Joint Pain by Keeping Bones Well Lubricated:
Hyaluronic acid supplements are effective at reducing joint pain in people with osteoarthritis. Injections can also be used but may come with risks.
Hyaluronic acid supplements can help increase skin moisture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical treatments can soothe redness and dermatitis, while injections can make skin appear firmer.
Can Speed Wound Healing:
Applying hyaluronic acid directly to an open wound can help speed up the recovery process. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effect.
Relieve Joint Pain by Keeping Bones Well Lubricated:
Hyaluronic acid supplements are effective at reducing joint pain in people with osteoarthritis. Injections can also be used but may come with risks.
 Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
A combination supplement containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate may help reduce the symptoms of acid reflux in some people.
Relieve Dry Eye and Discomfort:
Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
A combination supplement containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate may help reduce the symptoms of acid reflux in some people.
Relieve Dry Eye and Discomfort:
 Hyaluronic acid is naturally found in the eyes and often an ingredient in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effects.
Preserve Bone Strength:
Animal and test-tube research suggest that high doses of hyaluronic acid may help prevent bone loss, but no research has been conducted in humans.
Could Prevent Bladder Pain:
Hyaluronic acid can relieve bladder pain when inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter, but taking supplements by mouth may not have the same effects.
Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare Formulations:
Fortunately, when hyaluronic acid is applied topically, it takes very little to make a noticeable difference in helping aging skin recapture the appearance of youthful skin. In fact, it is so effective at retaining moisture it’s nearly impossible to add more than 2% HA to any formulation.
Sodium hyaluronate, another ingredient, is a salt that is derived from hyaluronic acid. The biggest difference between the two is that sodium hyaluronate absorbs into the skin much more readily than hyaluronic acid does.
Hyaluronic acid is naturally found in the eyes and often an ingredient in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effects.
Preserve Bone Strength:
Animal and test-tube research suggest that high doses of hyaluronic acid may help prevent bone loss, but no research has been conducted in humans.
Could Prevent Bladder Pain:
Hyaluronic acid can relieve bladder pain when inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter, but taking supplements by mouth may not have the same effects.
Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare Formulations:
Fortunately, when hyaluronic acid is applied topically, it takes very little to make a noticeable difference in helping aging skin recapture the appearance of youthful skin. In fact, it is so effective at retaining moisture it’s nearly impossible to add more than 2% HA to any formulation.
Sodium hyaluronate, another ingredient, is a salt that is derived from hyaluronic acid. The biggest difference between the two is that sodium hyaluronate absorbs into the skin much more readily than hyaluronic acid does.
 Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Hyaluronic acid is generally very safe to use, with few reported side effects.
Since the body naturally produces it, allergic reactions are very rare.
One study in 60 people with osteoarthritis who took 200 mg daily for one year reported no negative side effects.
However, its effects during pregnancy or breastfeeding have not been thoroughly studied, so these groups should be cautious and avoid supplementing with it.
There is also some evidence that cancer cells are sensitive to hyaluronic acid and taking supplements could make them grow faster.
For this reason, it is generally advised that people with cancer or a history of cancer avoid supplementing with it.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the skin or joints have a higher risk of side effects. However, negative reactions are mostly associated with the injection procedure, rather than hyaluronic acid itself.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Hyaluronic acid is generally very safe to use, with few reported side effects.
Since the body naturally produces it, allergic reactions are very rare.
One study in 60 people with osteoarthritis who took 200 mg daily for one year reported no negative side effects.
However, its effects during pregnancy or breastfeeding have not been thoroughly studied, so these groups should be cautious and avoid supplementing with it.
There is also some evidence that cancer cells are sensitive to hyaluronic acid and taking supplements could make them grow faster.
For this reason, it is generally advised that people with cancer or a history of cancer avoid supplementing with it.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the skin or joints have a higher risk of side effects. However, negative reactions are mostly associated with the injection procedure, rather than hyaluronic acid itself.



 Figure 1. Three types of medical applications of hyaluronan. HA, hyaluronan; OA, osteoarthritis; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection. The italic indicates future medical applications.
Hyaluronic acid has a low molecular weight and is considered the ideal natural moisturizing agent, so it is used as an additive in high-end makeup and as a moisturizer in creams, gels, lotions, masks, and serums. It is also used medically as a moisturizer to improve moisture retention and lubrication, and it also expands capillaries and improves skin health. For example, hyaluronic acid with a low molecular weight can be used as a lubricant in surgeries(such as knee surgery), while those with high molecular weight can be used as surgical lubricant and as a substitute for vitreous in ophthalmic surgery.
Figure 1. Three types of medical applications of hyaluronan. HA, hyaluronan; OA, osteoarthritis; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection. The italic indicates future medical applications.
Hyaluronic acid has a low molecular weight and is considered the ideal natural moisturizing agent, so it is used as an additive in high-end makeup and as a moisturizer in creams, gels, lotions, masks, and serums. It is also used medically as a moisturizer to improve moisture retention and lubrication, and it also expands capillaries and improves skin health. For example, hyaluronic acid with a low molecular weight can be used as a lubricant in surgeries(such as knee surgery), while those with high molecular weight can be used as surgical lubricant and as a substitute for vitreous in ophthalmic surgery. Figure 2.The water molecules which are hydrogen-bonded to HA stabilize the surfactant layer
When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behaviour suggest that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different.
Figure 2.The water molecules which are hydrogen-bonded to HA stabilize the surfactant layer
When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behaviour suggest that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different. Figure no 3. The cartilage matrix. The joint space is filled with synovial fluid. Glycosaminoglycans are attached to proteins, which are attached to a strand of hyaluronic acid to create a "bottle brush".
Figure no 3. The cartilage matrix. The joint space is filled with synovial fluid. Glycosaminoglycans are attached to proteins, which are attached to a strand of hyaluronic acid to create a "bottle brush". Figure 4. Hyaluronic acid is composed of alternating residues of β-D-(1‑3) glucuronic acid and β-D-(1‑4)-N-acetylglucosamine.
Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction(intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues.
Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuverer and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation.
Figure 4. Hyaluronic acid is composed of alternating residues of β-D-(1‑3) glucuronic acid and β-D-(1‑4)-N-acetylglucosamine.
Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction(intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues.
Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuverer and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation. Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
It is the result of two biologically independent processes. The first is intrinsic or innate aging, an unpreventable process, which affects the skin in the same pattern as it affects all internal organs. The second is extrinsic aging, which is the result of exposure to external factors, mainly ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, that is also referred to as photoaging.
Skin aging is also associated with loss of skin moisture. The key molecule involved in skin moisture is hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a unique capacity to bind and retain water molecules.
Promotes Healthier, More Supple Skin:
Anti-Aging and Moisturizing:
It is the result of two biologically independent processes. The first is intrinsic or innate aging, an unpreventable process, which affects the skin in the same pattern as it affects all internal organs. The second is extrinsic aging, which is the result of exposure to external factors, mainly ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, that is also referred to as photoaging.
Skin aging is also associated with loss of skin moisture. The key molecule involved in skin moisture is hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a unique capacity to bind and retain water molecules.
Promotes Healthier, More Supple Skin:
 Hyaluronic acid supplements can help increase skin moisture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical treatments can soothe redness and dermatitis, while injections can make skin appear firmer.
Can Speed Wound Healing:
Applying hyaluronic acid directly to an open wound can help speed up the recovery process. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effect.
Relieve Joint Pain by Keeping Bones Well Lubricated:
Hyaluronic acid supplements are effective at reducing joint pain in people with osteoarthritis. Injections can also be used but may come with risks.
Hyaluronic acid supplements can help increase skin moisture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Topical treatments can soothe redness and dermatitis, while injections can make skin appear firmer.
Can Speed Wound Healing:
Applying hyaluronic acid directly to an open wound can help speed up the recovery process. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effect.
Relieve Joint Pain by Keeping Bones Well Lubricated:
Hyaluronic acid supplements are effective at reducing joint pain in people with osteoarthritis. Injections can also be used but may come with risks.
 Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
A combination supplement containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate may help reduce the symptoms of acid reflux in some people.
Relieve Dry Eye and Discomfort:
Soothe Acid Reflux Symptoms:
A combination supplement containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate may help reduce the symptoms of acid reflux in some people.
Relieve Dry Eye and Discomfort:
 Hyaluronic acid is naturally found in the eyes and often an ingredient in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effects.
Preserve Bone Strength:
Animal and test-tube research suggest that high doses of hyaluronic acid may help prevent bone loss, but no research has been conducted in humans.
Could Prevent Bladder Pain:
Hyaluronic acid can relieve bladder pain when inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter, but taking supplements by mouth may not have the same effects.
Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare Formulations:
Fortunately, when hyaluronic acid is applied topically, it takes very little to make a noticeable difference in helping aging skin recapture the appearance of youthful skin. In fact, it is so effective at retaining moisture it’s nearly impossible to add more than 2% HA to any formulation.
Sodium hyaluronate, another ingredient, is a salt that is derived from hyaluronic acid. The biggest difference between the two is that sodium hyaluronate absorbs into the skin much more readily than hyaluronic acid does.
Hyaluronic acid is naturally found in the eyes and often an ingredient in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms. It’s unknown whether supplementing with it would have the same effects.
Preserve Bone Strength:
Animal and test-tube research suggest that high doses of hyaluronic acid may help prevent bone loss, but no research has been conducted in humans.
Could Prevent Bladder Pain:
Hyaluronic acid can relieve bladder pain when inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter, but taking supplements by mouth may not have the same effects.
Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare Formulations:
Fortunately, when hyaluronic acid is applied topically, it takes very little to make a noticeable difference in helping aging skin recapture the appearance of youthful skin. In fact, it is so effective at retaining moisture it’s nearly impossible to add more than 2% HA to any formulation.
Sodium hyaluronate, another ingredient, is a salt that is derived from hyaluronic acid. The biggest difference between the two is that sodium hyaluronate absorbs into the skin much more readily than hyaluronic acid does.
 Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Hyaluronic acid is generally very safe to use, with few reported side effects.
Since the body naturally produces it, allergic reactions are very rare.
One study in 60 people with osteoarthritis who took 200 mg daily for one year reported no negative side effects.
However, its effects during pregnancy or breastfeeding have not been thoroughly studied, so these groups should be cautious and avoid supplementing with it.
There is also some evidence that cancer cells are sensitive to hyaluronic acid and taking supplements could make them grow faster.
For this reason, it is generally advised that people with cancer or a history of cancer avoid supplementing with it.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the skin or joints have a higher risk of side effects. However, negative reactions are mostly associated with the injection procedure, rather than hyaluronic acid itself.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Hyaluronic acid is generally very safe to use, with few reported side effects.
Since the body naturally produces it, allergic reactions are very rare.
One study in 60 people with osteoarthritis who took 200 mg daily for one year reported no negative side effects.
However, its effects during pregnancy or breastfeeding have not been thoroughly studied, so these groups should be cautious and avoid supplementing with it.
There is also some evidence that cancer cells are sensitive to hyaluronic acid and taking supplements could make them grow faster.
For this reason, it is generally advised that people with cancer or a history of cancer avoid supplementing with it.
Hyaluronic acid injections into the skin or joints have a higher risk of side effects. However, negative reactions are mostly associated with the injection procedure, rather than hyaluronic acid itself.






![Red Onion Oil 🧅 Reduces Hair Fall & Accelerates Hair Regrowth [پیاز کا تیل].. Trending.... 🔥 - ChiltanPure](http://chiltanpure.com/cdn/shop/products/red-onion-oil-reduces-hair-fall-amp-accelerates-hair-regrowth-piaz-ka-til-trending-394813_165x.jpg?v=1707464619)
![Red Onion Oil 🧅 Reduces Hair Fall & Accelerates Hair Regrowth [پیاز کا تیل].. Trending.... 🔥 - ChiltanPure](http://chiltanpure.com/cdn/shop/products/red-onion-oil-reduces-hair-fall-amp-accelerates-hair-regrowth-piaz-ka-til-trending-329640_165x.jpg?v=1708127491)














