CARRIER OILS - A DETAILED GUIDE TO TYPES, BENEFITS, USES & MORE!
by
Muhammad Zohaib
27 Jul 2022
Carrier oils are safe enough to use directly on the skin and can be used to dilute essential oils Carrier oils are miracle workers in their own right. Most contain essential fatty acids, vitamins, and nutrients that do amazing things for our hair and skin. Carrier oils are also often anti-inflammatory, rich in antioxidants and humectants, meaning they keep the skin hydrated Carrier oil is a Vital Aspect of Aromatherapy.
INTRODUCTION
"Carrier Oil" is a term given to base oils that dilute essential oils before topical application, potent to apply directly to the skin. Despite being referred to as vegetable oils, not all Carrier Oils are derived from vegetables, pressed from seeds, nuts, or kernels. Carrier Oils are also called "fixed oils" because they do not quickly evaporate from the skin's surface and are fixed" on the skin.
A Carrier Oil is a vital aspect of an aromatherapy massage or a natural cosmetic. It can affect the benefits and usefulness of the essential oils and the color, scent, therapeutic properties, and final product's shelf life.
Each Carrier Oil comprises different components characteristics, such as color, viscosity, and penetration speed, while offering therapeutic properties.
WHAT ARE CARRIER OILS?
Carrier Oils have been used since ancient Greece and Rome when aromatic oils were used in massages, baths, cosmetics, and medical applications. In the 1950s, Marguerite Maury, the first person to use individually prescribed combinations of essential oils for the individual's desired therapeutic benefits, began diluting essential oils in a vegetable Carrier Oil and massaging them into the skin by using a Tibetan technique that applies pressure along the spine.
"Carrier Oil" is generally used in the contexts of aromatherapy and cosmetic recipes for natural skin and hair care. It refers to base oils that dilute essential oils before topical application, as the latter is much too potent to apply directly to the skin.
Despite also being referred to as vegetable oils, not all Carrier Oils are derived from vegetables; many are pressed from seeds, nuts, or kernels. Carrier Oils have also earned the moniker "fixed oils" because they remain fixed on the skin. This means that, unlike essential oils, they do not quickly evaporate from the skin's surface or have the strong, natural scent of plants, making them ideal for controlling critical oil concentration and reducing the strength of an essential oil's aroma without altering its therapeutic properties.
A Carrier Oil is a vital aspect of an aromatherapy massage or a natural cosmetic such as a bath oil, body oil, cream, lip balm, lotion, or another moisturizer, as it can affect the usefulness of the massage and the color, scent, therapeutic properties, and shelf life of the final product. By providing the lubrication required for a massage, the light, and non-sticky Carrier Oils effectively allow the hands to glide easily over the skin while penetrating the skin and carrying the essential
Oils into the body. Carrier Oils can also prevent the potential irritation, sensitization, redness, or burning that can be caused by the undiluted use of Essential Oils.
COMPOSITION OF CARRIER OILS
Each Carrier Oil is comprised of different components that demonstrate distinct characteristics, such as color, viscosity, and penetration speed, offering variable combinations of therapeutic properties; thus, they have valuable effects even when used on their own. Carrier Oils generally contain components such as fat-soluble vitamins, minerals, Fatty Acid antioxidants, and other nutrients that improve the look and feel of skin and hair by adding moisture, soothing irritation, and reducing the effects of dryness. The choice of a Carrier Oil is dependent on the desired result.
Carrier Oil varieties, these are the main constituents in most varieties:
| Minerals |
• Brighten dull complexion
• Protect against environmental stressor
• Balance oil production while gentle on sensitive skin
• Uplift exfoliation
• Firm and tighten skin for smoother appearance
• Maintain skin’s moisturizer level
|
| Vitamins |
• repair vital skin tissue
• Control acne
• Reduce lines and wrinkles
• Hydrate skin to cheer a healthy glow
• Exhibit anti-inflammatory properties
• Even out skin tone
|
| Sterolins |
• Reduce age spots
• Repair sun damaged skin
• Reduce the appearance of scars
• Moisturize, Smooth and soften skin and hair
|
| Oleic Acids |
• Maintain the softness, suppleness, and radiance of skin and hair
• Stimulate the growth of thicker, longer and stronger hair
• Reduce the appearance of aging, premature wrinkles and fine lines
• Eliminate dandruff and thereby support hair growth
• Boost immunity
|
| Linoleic Acids |
• Moisturize hair and promote growth
• wound healing
• Be an effective emulsifier in the formulation of soaps and quick-drying oils
• Exhibit anti-inflammatory properties
• Soothe acne and reduce chances of outbreaks
• Promote moisture retention in skin and hair
• Make oils feel thinner in consistency, thus being beneficial for use on acne-prone skin
|
| Vitamin E |
• Exhibit anti-oxidant activity
• Repair and improve the appearance of damaged tissue
|
| Lecithin |
• Soften and soothe the skin and hair
• Keep dry, brittle skin and hair hydrated, restoring the moisture and luster
• Increase circulation and enhance the health and strength of the hair and skin
|
| Phytosterols |
• Boost collagen production
• Relieve skin of sun damage
• Promote the growth of newer, firmer skin
• Boost immunity
• Minimize the appearance of scars and other unwanted blemishes
|
|
Essential Fatty Acids
|
• Maintain the skin's natural oil barrier
• Hydrate skin
• promote a supple, youthful appearance
• Nourish cells and eliminate bodily toxins
• Protect skin by creating an antimicrobial against harsh environmental elements
• Prevent the premature signs of aging
• Reduce water loss through the skin’s surface
• Enhance the texture and softness of skin and hair
|
|
Selenium
|
- Exhibit anti-oxidant activity
- Reduce the appearance of wrinkles
- Facilitate the healing of burns, wounds.
|
| Medium-Chain Triglycerides |
- Eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi
- Offer intense moisture
- eliminate dandruff
- Boost hair growth
- Conditioned hair
|
| Palmitoleic Acid |
- Delay the appearance of premature aging
- Moisturize and tighten the skin
- Promote the growth of shiny hair
- Enhance the brightness of the complexion
- Boost the growth of healthy-looking nails
- Enhance skin elasticity to prevent symptoms of premature aging, such as wrinkles
|
EXTRACTING CARRIER OILS
Although true Carrier Oils are obtained mostly from nuts and seeds, there are a few exceptions to this – Coconut Oil, for example, is extracted from its ‘khopra’ which is the white inner flesh, and Jojoba Oil, which is actually a liquid wax, is extracted from a shrub that has leathery leaves. To obtain oils from nuts and seeds, they undergo one of the following processes:
- Cold Pressing
- Expeller Pressing
- Oil Maceration
- Solvent Extraction
Cold Pressing
Chemical-free process that involves placing the nuts or seeds in a horizontal press that has an 'expeller,' which is a rotating screw. The screw drives the nuts and seeds through a barrel-shaped hollow and compresses them until the high pressure squeezes out the oil, which seeps out through the opening, while the ‘meal,’ or the debris, remains inside the barrel. The oil is then filtered, resulting in the finished product. Due to the absence of solvent residues in Cold Pressing, the outcome is cleaner, purer oils that are higher in natural colors and scents. The friction that is created, some heat is produced during this process, despite its name; however, this heat causes little damage to the oil. The hardness of the nuts or the seeds being pressed determines the temperature of this produced heat. The harder the nuts or seeds, the higher the required pressure to extract their oils, which results in higher friction and thus higher heat.
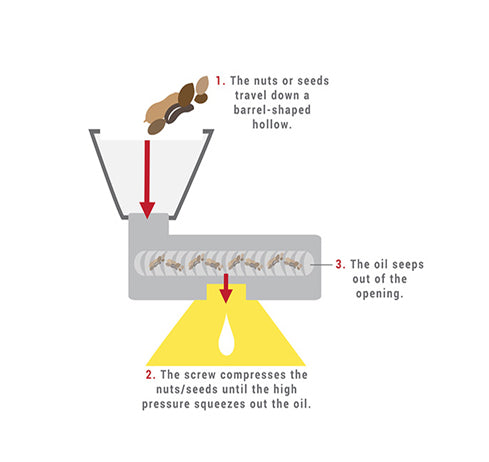
Expeller Pressing
Mechanical processing method of extraction that is similar to Cold Pressing in that it involves the use of a hydraulic press that generates heat. Important to note that all Cold Pressed Oils are Expeller Pressed, but that all Expeller Pressed oils are not unavoidably Cold Pressed. Oils that have undergone only Expeller Pressing have not been processed to maintain low heat levels and this can potentially damage an oil’s delicate nutrients.
Expeller Pressed oils are typically RDB, which stands for “Refined, Bleached, and Deodorized.” This refinement process helps to remove impurities, improve the color or texture, or stabilize the shelf life, making these oils suitable and economical for use as cosmetic bases.
Refining involves introducing the oil to a weak base solution to turn the free fatty acids into soap. It is centrifuged and washed with water until the pure oil remains.
Bleaching involves removing or improving the oil’s color and clarity by passing it through an earth or clay and filtering the oil.
Deodorizing removes unpleasant or strong odors by vaporizing the oil and vacuuming its volatile aromatic substances.
Winterization, which involves cooling a Carrier Oil and filtering it to remove the solid crystallized portions in order to achieve a lighter, clearer oil.
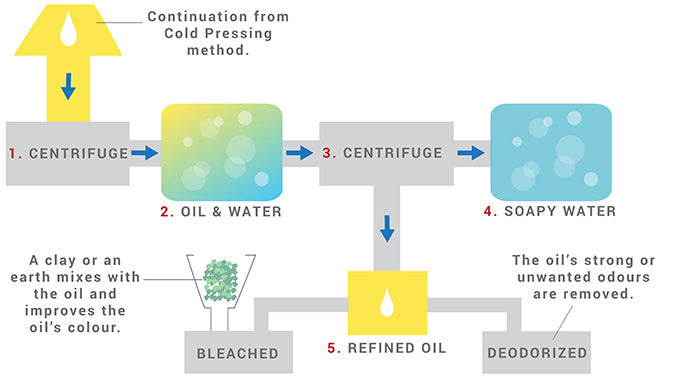 Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.
Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.
QUALITY OF CARRIER OILS
A high-quality Carrier Oil will be as natural and as unadulterated as possible and it will ideally be Cold Pressed. Organic Carrier Oils are most commonly perceived to be of the highest quality, these will eventually go rancid over time. The quality of an oil can be determined by the following factors
- Aroma,
- Method of Extraction,
- Consistency and Rate ofAbsorption,
- Natural Fatty Acids
- Tocopherols, and Shelf Life, among other characteristics.
- Aroma
Typically, Carrier Oils are either odorless or they have mild, distinctive aromas that are faintly nutty, sweet, and/or characteristic of the nut or seed from which they are derived.
Method of Extraction
The ideal Carrier Oil for use in natural products is a Cold Pressed (Raw), Organic, Unrefined, Extra Virgin oil. Carrier Oils that are truly “raw” will not have been heated more than 45 ᵒC. Carrier Oils that are unrefined will have been filtered to eliminate dust or small particles without compromising the oil’s nutrients, vitamins, and fatty acids. Extra Virgin Carrier Oils will have only been pressed one time.
Consistency And Absorption
The consistency of various Carrier Oils can be either thick or thin. The choice of either viscosity is a matter of personal preference. A light oil with fast absorption and an absence of a greasy residue would be a high-quality oil for oily skin or hair, as it would penetrate the skin quickly without clogging pores. On the other hand, a rich, deeply moisturizing oil is of better quality for treating severely dry and damaged skin or hair.
Natural Fatty Acids and Tocopherols
Carrier Oils contain beneficial and restorative fatty acids that lend the oils their nourishing and moisturizing properties. These are the constituents that offer regenerative and stimulating properties to promote the look and feel of younger, fresher, and healthier hair and skin. Tocopherols such as natural Vitamin E act as natural preservatives. Carrier Oils have a high nutrient content but are too rich to use on their own or their odors are too overpowering. In these situations, they can be diluted in other Carrier Oils to customize and create the ideal Carrier Oil, several can be blended to also change or combine their therapeutic properties before application.
STORAGE OF CARRIER OIL
Many rules for storing essential oils also apply to storing Carrier Oils. Specifically, they should be stored in cool, dark places away from strong and direct light, especially sunlight. Although refrigeration is acceptable for most oils and although it helps preserve freshness there are some oils, such as Avocado, that should not be refrigerated, as this can negatively affect some of the oil’s significant, delicate constituents. After refrigeration, some oils may appear to be solid or cloudy, but their clarity will be restored once they return to room temperature.
TYPES OF CARRIER OILS
Carrier Oils can be categorized by their solidity: Hard and Soft
Hard oils are Solid at room temperature, they must be melted into a liquid state. Hard oils add firmness to a finished product, and without a sufficient amount of a hard oil, a product such as a soap bar will feel soft or sticky. The most popular hard oils are: Palm and Coconut.
Soft oils are liquid at room temperature. They add nourishing and moisturizing properties to a finished product. Without a sufficient amount of a soft oil, a product such as a soap bar will be brittle and will begin to crack. The most popular soft oils are: Olive, Canola, Rice bran, and Sweet Almond.
| Type Of Oil |
Benefits |
Carrier Oils |
|
Nut Oils
|
- Extremely emollient and soothing for sensitive, dry, inflamed and sore skin
- Efficient in face mask treatments for acne-prone skin
- Stimulate circulation
- Anti-inflammatory
- Facilitate wound healing
- Maintain skin tightness and elasticity
|
- Almond
- Hazelnut
- Macadamia
- Walnut
|
|
Seed Oils
|
- Condition skin to rejuvenate complexion, especially in mature or prematurely aging skin
- Repair damage caused by dryness
- Soothe itching and discomfort caused by burns
- Reduce appearance of scarring
|
- Baobab
- Black Currant
- Borage
- Broccoli
- Carrot
|
|
Fruit Oils
|
- Gentle and nourishing
- Light in texture to moisturize without leaving a greasy residue
- Reduce the appearance of aging skin
- Suitable for sensitive skin
- Cleansing and softening
- Exhibits anti-oxidant properties
|
- Apricot
- Avocado
- Grape Seed
- Peach Kernel
- Olive
|
|
Essential Fatty Acid Oils
|
- Hydrate and soothe itchy, dry, inflamed, and acne-prone skin
- Anti-inflammatory, Anti-bacterial, Anti-fungal, Anti-septic
- Balance essential fatty acid deficiency and skin’s oil production
- Balance hormones
- Demonstrate reparative and astringent properties that facilitate wound healing
|
|
CARRIER OILS USES & BENEFITS
Although seemingly counterintuitive, it is necessary for essential oils to be diluted in order to work effectively, and that is why Carrier Oils are required. There are a few exceptions to the fact that essential oils will harm the body if applied neat, it is best to dilute them with a Carrier Oil before use, otherwise, the resulting bodily harm will make waste of the essential oil, the effort, and the money spent. Aside from enhancing skin’s absorption of essential oils, Carrier Oils offer therapeutic properties through their beneficial components, including nourishing constituents that our bodies cannot produce on their own, such as essential fatty acids.
Absorption Rates of Carrier Oil
| ABSORPTION RATE |
FINISH ON SKIN |
CARRIER OILS
|
| Very Fast |
THESE OILS ARE
- Considered to be drying, because they are quickly absorbed by skin and do not leave a greasy residue
- High in polyunsaturated fats
|
LOOK FOR
- Hazelnut (CP)
- Rosehip (Extra Virgin, CP)
|
|
Fast
|
- These light oils are quickly absorbed by skin but leave a smooth, silky finish. Skin will feel moisturized rather than greasy
|
- Apricot Kernel (CP)
- Camellia Seed (CP)
- Grape Seed
- Meadow foam
- Safflower
- Canola
- Fractionated Coconut
- Prickly Pear
- Broccoli Seed
|
|
Average
|
- These oils leave a silky feeling on the skin
|
- Hemp Seed (Unrefined, CP)
- Jojoba (CP)
- Argan
- Babassu
- Raspberry Seed
- Sesame
|
|
Slow
|
- These oils could feel gummy or waxy before they warm up to body temperature. They tend to leave skin with a slight oily residue
|
- Carrot (Macerated, CP)
- Pomegranate (Refined, CP)
- Sea Buckthorn (CO2)
- Black Currant Seed
- Tamanu (Madagascar, CP)
- Avocado (Refined, CP)
- Castor
- Oat
- Flax Seed (CP)
- Sweet Almond (Sweet Virgin, CP)
- Kuikui Nut (CP)
- Olive (Extra Virgin, CP)
- Sunflower (CP)
|
|
Very Slow
|
- These oils may need to have gentle heat applied to them before use. They tend to feel heavy on the skin and leave a thick, oily, and moisturizing barrier on the skin but are absorbed by the skin eventually
- Higher in saturated fats and have a longer shelf life than those that dry quickly
|
- Evening Primrose (CP)
- Neem (CP)
- Palm (Refined, CP)
- Borage (Unrefined, CP)
- Coconut (Refined, CP)
- Macadamia Nut (CP)
|
*These rates are general and may vary between suppliers, as the speed of absorption depends on the method of extraction. These are largely New Directions Aromatics’ Carrier Oil absorption rates.
SHELF LIFE OF CARRIER OILS
Carrier Oils that are high in unsaturated fatty acid content will generally have a shorter shelf life and can last up to 6 months, whereas oils with a longer shelf life can last 1-2 years, maintain an oil’s quality and maximize its shelf life, it should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark place.
Carrier Oils with natural antioxidant properties, such as those with high Vitamin E or Lauric Acid content, have longer shelf lives, as these constituents either prevent oxidation or slow down the process. Other Carrier Oils can be combined with these antioxidant Carrier Oils to have their shelf lives increased.
Sample Block Quote
Praesent vestibulum congue tellus at fringilla. Curabitur vitae semper sem, eu convallis est. Cras felis nunc commodo eu convallis vitae interdum non nisl. Maecenas ac est sit amet augue pharetra convallis.
Sample Paragraph Text
Praesent vestibulum congue tellus at fringilla. Curabitur vitae semper sem, eu convallis est. Cras felis nunc commodo eu convallis vitae interdum non nisl. Maecenas ac est sit amet augue pharetra convallis nec danos dui. Cras suscipit quam et turpis eleifend vitae malesuada magna congue. Damus id ullamcorper neque. Sed vitae mi a mi pretium aliquet ac sed elitos. Pellentesque nulla eros accumsan quis justo at tincidunt lobortis deli denimes, suspendisse vestibulum lectus in lectus volutpate.
 Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.
Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.
 Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.
Oil Maceration
Botanicals used that do not hold a sufficient amount of oil to be obtained through the pressing methods. One of the advantages of this method is that the resulting oils retain the pleasant fragrances of the botanical matter used, and these scents can be imparted to skincare products.
Macerated Oil is a vegetable oil that is used in the same manner as a solvent or a base oil in order to extract the fat-soluble properties of other botanical materials and become infused with their therapeutic properties. For this reason, a Macerated Oil is sometimes referred to as an Infused Oil. The most commonly used base oils are Olive or Sunflower Oils. Refined oils are ideal for use in natural cosmetics, as oils with dark colors and strong odors can negatively impact a finished cosmetic product.
Solvent Extraction
That is applied to Carrier Oils in the same way it is applied to essential oils. It involves soaking botanical material in a solvent such as Ethanol, Petroleum Ether, Hexane, or Methanol. The cell membranes of the plant matter are ruptured and its oils are synthesized with the solvent. The solvent is then filtered out and the resulting oil is bottled. A low concentration of solvent residues can remain in the oil, thus preventing it from being 100% pure.




![Red Onion Oil 🧅 Reduces Hair Fall & Accelerates Hair Regrowth [پیاز کا تیل].. Trending.... 🔥 - ChiltanPure](http://chiltanpure.com/cdn/shop/products/red-onion-oil-reduces-hair-fall-amp-accelerates-hair-regrowth-piaz-ka-til-trending-394813_165x.jpg?v=1707464619)
![Red Onion Oil 🧅 Reduces Hair Fall & Accelerates Hair Regrowth [پیاز کا تیل].. Trending.... 🔥 - ChiltanPure](http://chiltanpure.com/cdn/shop/products/red-onion-oil-reduces-hair-fall-amp-accelerates-hair-regrowth-piaz-ka-til-trending-329640_165x.jpg?v=1708127491)













1 comment
Thank you for sharing valuable insights about carrier oils! At EssentialNaturalOils.com, we understand the importance of these oils in aromatherapy and skincare. Our premium collection offers high-quality carrier oils to enhance your beauty and wellness routines. Explore our range https://www.essentialnaturaloils.com/pages/carrier-oils for natural nourishment and hydration.
Regards:
CEO